Overview#
PyVista is:
Pythonic VTK: a high-level API to the Visualization Toolkit (VTK)
mesh data structures and filtering methods for spatial datasets
3D plotting made simple and built for large/complex data geometries
PyVista is a helper library for the Visualization Toolkit (VTK) that takes a different approach on interfacing with VTK through NumPy and direct array access. This package provides a Pythonic, well-documented interface exposing VTK’s powerful visualization backend to facilitate rapid prototyping, analysis, and visual integration of spatially referenced datasets.
This module can be used for scientific plotting for presentations and research papers as well as a supporting module for other mesh dependent Python modules.
Want to test-drive PyVista? Check out our live examples on MyBinder:
Brief Examples#
Here are some brief interactive examples that demonstrate how you might want to use PyVista:
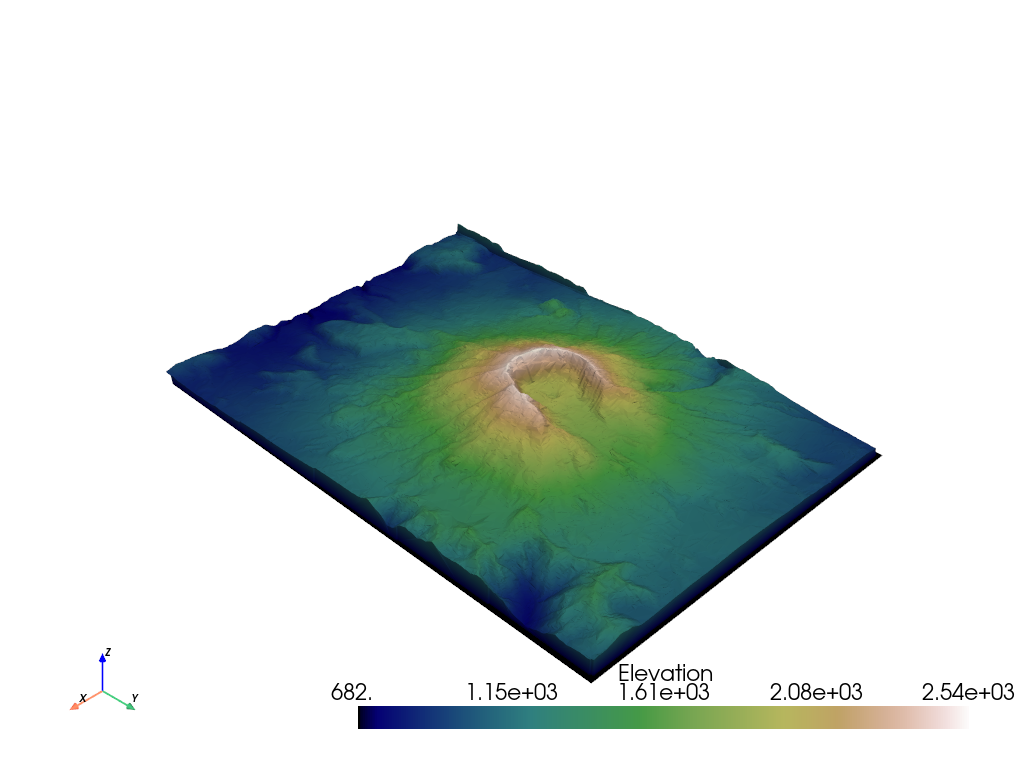
Maps and Geoscience#
Download the surface elevation map of Mount St. Helens and plot it.
from pyvista import examples
mesh = examples.download_st_helens()
warped = mesh.warp_by_scalar('Elevation')
surf = warped.extract_surface().triangulate()
surf = surf.decimate_pro(0.75) # reduce the density of the mesh by 75%
surf.plot(cmap='gist_earth')
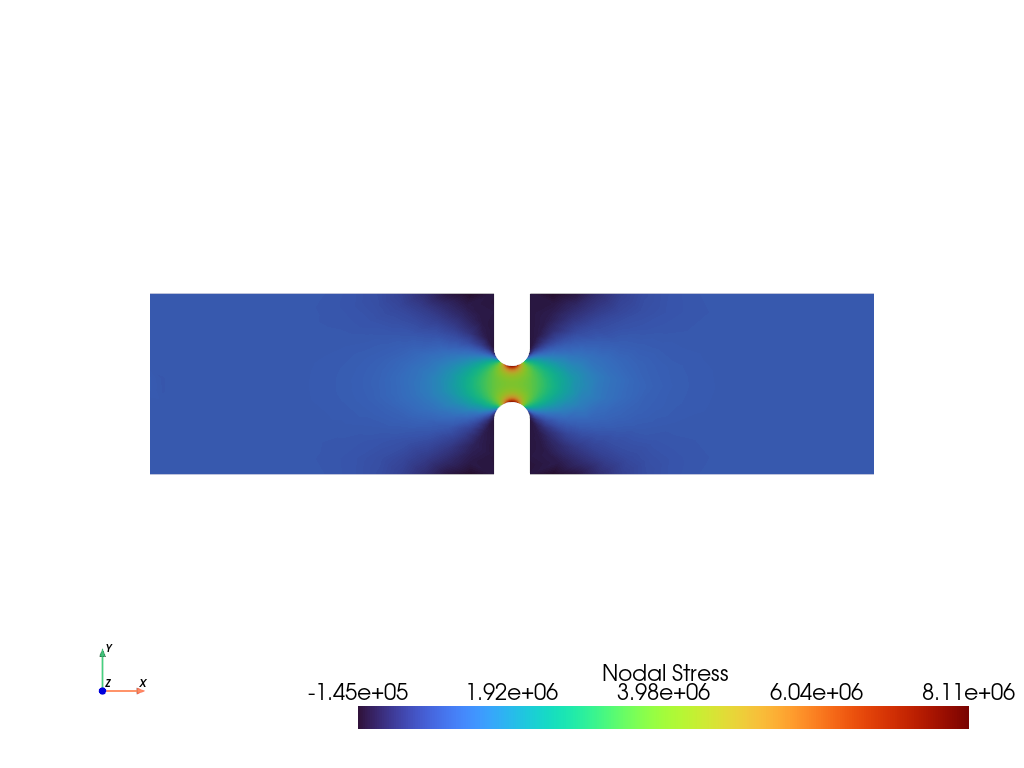
Finite Element Analysis#
Plot the ‘X’ component of elastic stress of a 3D notch specimen.
from pyvista import examples
mesh = examples.download_notch_stress()
mesh.plot(scalars='Nodal Stress', component=0, cmap='turbo', cpos='xy')
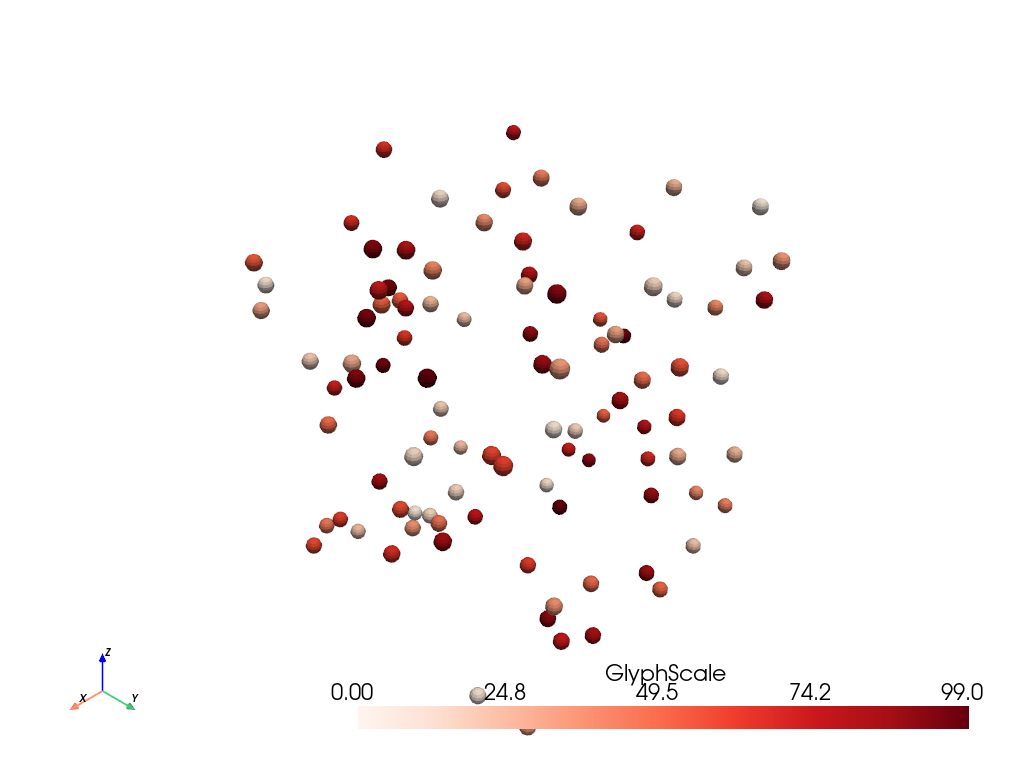
Simple Point Cloud with NumPy#
Easily integrate with NumPy and create a variety of geometries and plot them. You could use any geometry to create your glyphs, or even plot the points directly.
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)
point_cloud = rng.random((100, 3))
pdata = pv.PolyData(point_cloud)
pdata['orig_sphere'] = np.arange(100)
# create many spheres from the point cloud
sphere = pv.Sphere(radius=0.02, phi_resolution=10, theta_resolution=10)
pc = pdata.glyph(scale=False, geom=sphere, orient=False)
pc.plot(cmap='Reds')
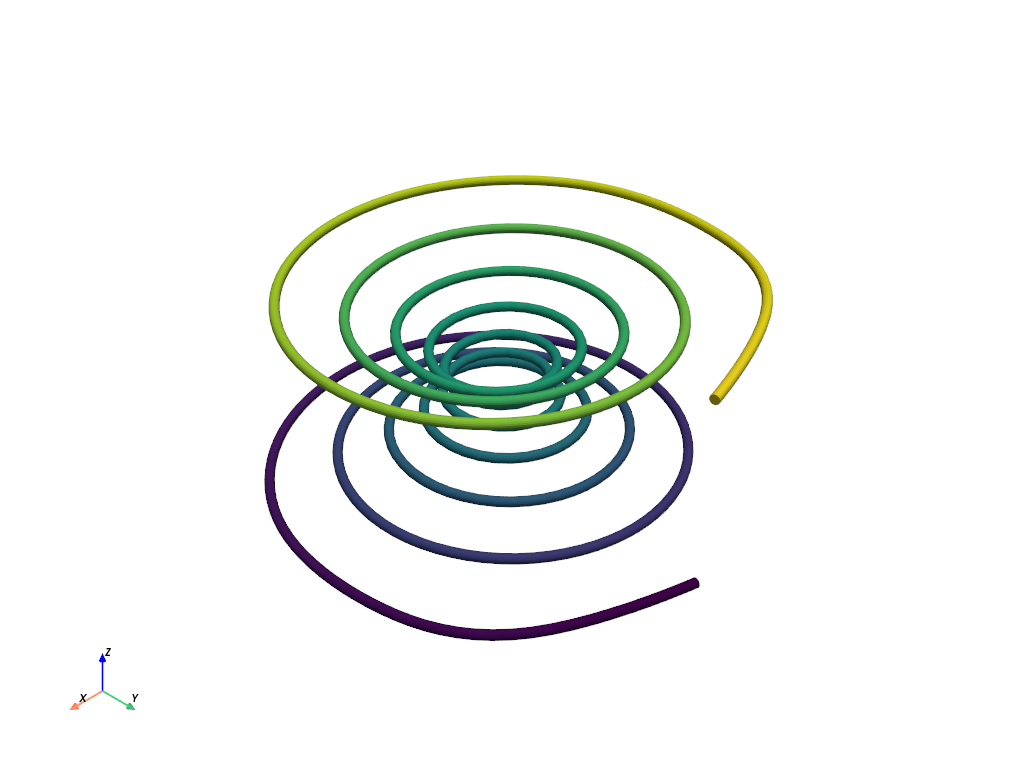
Plot a Spline#
Generate a spline from an array of NumPy points.
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
# Make the xyz points
theta = np.linspace(-10 * np.pi, 10 * np.pi, 100)
z = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100)
r = z**2 + 1
x = r * np.sin(theta)
y = r * np.cos(theta)
points = np.column_stack((x, y, z))
spline = pv.Spline(points, 500).tube(radius=0.1)
spline.plot(scalars='arc_length', show_scalar_bar=False)
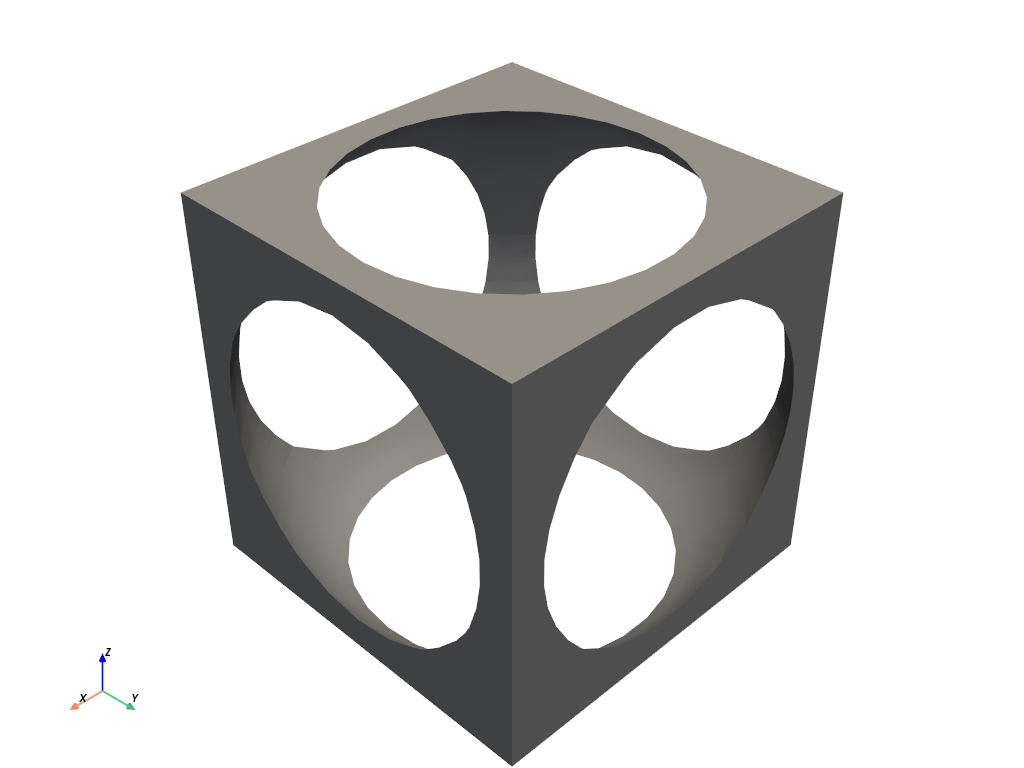
Boolean Operations on Meshes#
Subtract a sphere from a cube mesh.
import pyvista as pv
import numpy as np
def make_cube():
x = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, 25)
grid = pv.StructuredGrid(*np.meshgrid(x, x, x))
surf = grid.extract_surface().triangulate().flip_faces()
return surf
# Create example PolyData meshes for boolean operations
sphere = pv.Sphere(radius=0.65, center=(0, 0, 0))
cube = make_cube()
# Perform a boolean difference
boolean = cube.boolean_difference(sphere)
boolean.plot(color='darkgrey', smooth_shading=True, split_sharp_edges=True)
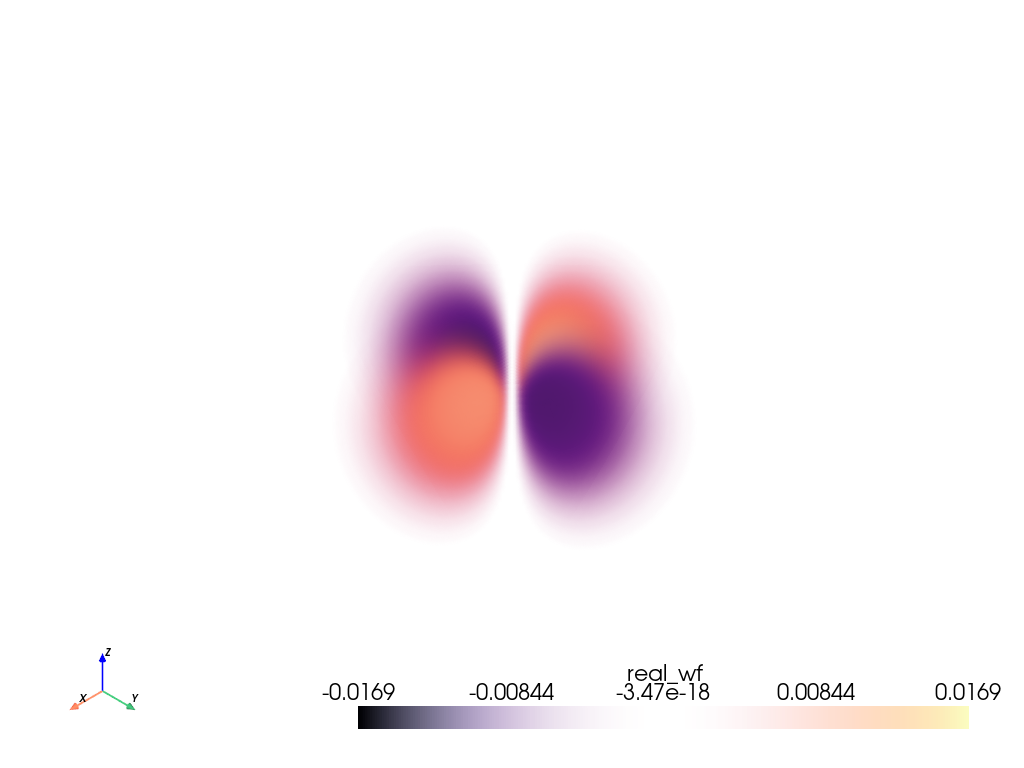
Plot Volumetric Data#
Plot the \(3d_{xy}\) orbital of a hydrogen atom.
Note
This example requires sympy.
from pyvista import examples
grid = examples.load_hydrogen_orbital(3, 2, -2)
grid.plot(volume=True, opacity=[1, 0, 1], cmap='magma')
Translating#
The recommended way for new contributors to translate PyVista’s documentation is to join the translation team on Transifex.
There is a pyvista translation page for pyvista (main) documentation.
Login to transifex service.
Go to pyvista translation page.
Click
Request languageand fill form.Wait acceptance by transifex pyvista translation maintainers.
(After acceptance) Translate on transifex.
We can host the translated document using atsphinx-mini18n.
Translation is backed up in pyvista-doc-translations.
Details can be found here: https://help.transifex.com/en/
Status#
Professional Support#
PyVista is a community-driven Open Source project, but many users and organizations rely on it in production workflows, research pipelines, and custom visualization systems. If you need expert guidance, development help, or guaranteed support, there are several ways to engage with the people who build and maintain PyVista.
For general inquiries, reach out to info@pyvista.org and we can help connect you with the right community experts for your 3D visualization or analysis needs.
If you are looking for professional services (consulting, custom development, feature design, integration support, or training), consider sponsoring PyVista’s core developers through the “Sponsor this project” section on GitHub. Sponsorship not only provides direct access to experts but also helps sustain critical maintenance and ongoing feature work that keeps PyVista reliable and modern.
More details can be found in the discussion post: pyvista/pyvista#4033
Sponsoring a developer supports both your project and the health of the PyVista ecosystem, ensuring continued improvements, long-term stability, and expert help when you need it.