pyvista.ImageDataFilters.crop#
- ImageDataFilters.crop(
- *,
- factor: float | VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- margin: int | VectorLike[int] | None = None,
- offset: VectorLike[int] | None = None,
- dimensions: VectorLike[int] | None = None,
- extent: VectorLike[int] | None = None,
- normalized_bounds: VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- mask: str | ImageData | NumpyArray[float] | Literal[True] | None = None,
- padding: int | VectorLike[int] | None = None,
- background_value: float | None = None,
- keep_dimensions: bool = False,
- fill_value: float | VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- rebase_coordinates: bool = False,
- progress_bar: bool = False,
Crop this image to remove points at its boundaries.
This filter is useful for extracting a volume or region of interest. There are several ways to crop:
Use
factorto crop a portion of the image symmetrically.Use
marginto remove points from the image border.Use
dimensions(and optionally,offset) to explicitly crop to the specifieddimensionsandoffset.Use
extentto explicitly crop to a specifiedextent.Use
normalized_boundsto crop a bounding box relative to the input size.Use
mask,padding, andbackground_valueto crop to this mesh using scalar values to define the cropping region.
These methods are all independent, e.g. it is not possible to specify both
factorandmargin.By default, the cropped output’s
dimensionsare typically less than the input’s dimensions. Optionally, usekeep_dimensionsandfill_valueto ensure the output dimensions always match the input.Note
All cropping is performed using the image’s ijk-indices, not physical xyz-bounds.
Added in version 0.46.
- Parameters:
- factor
float,optional Cropping factor in range
[0.0, 1.0]which specifies the proportion of the image to keep along each axis. Use a single float for uniform cropping or a vector of three floats for cropping each xyz-axis independently. The crop is centered in the image.- margin
int|VectorLike[int],optional Margin to remove from each side of each axis. Specify:
A single value to remove from all boundaries equally.
Two values, one for each
(X, Y)axis, to remove margin from each axis independently.Three values, one for each
(X, Y, Z)axis, to remove margin from each axis independently.Four values, one for each
(-X, +X, -Y, +Y)boundary, to remove margin from each boundary independently.Six values, one for each
(-X, +X, -Y, +Y, -Z, +Z)boundary, to remove margin from each boundary independently.
- offset
VectorLike[int],optional Length-3 vector of integers specifying the
offsetindices where the cropping region originates. If specified, thendimensionsmust also be provided.- dimensions
VectorLike[int],optional Length-3 vector of integers specifying the
dimensionsof the cropping region.offsetmay also be provided, but if it is not, the crop is centered in the image.- extent
VectorLike[int],optional Length-6 vector of integers specifying the full
extentof the cropping region.- normalized_bounds
VectorLike[float],optional Normalized bounds relative to the input. These are floats between
0.0and1.0that define a box relative to the input size. The input is cropped such that it fully fits within these bounds. Has the form(x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max, z_min, z_max).- mask
str|ImageData|NumpyArray[float] | bool,optional Scalar values that define the cropping region. Set this option to:
a string denoting the name of scalars belonging to this mesh
Trueto use this mesh’s default scalarsa separate image, in which case the other image’s active scalars are used
a 1D or 2D (multi-component) array
The length of the scalar array must equal the number of points.
This mesh will be cropped to the bounds of the foreground values of the array, i.e. values that are not equal to the specified
background_value.- padding
int|VectorLike[int],optional Padding to add to foreground region before cropping. Only valid when using a mask to crop the image. Specify:
A single value to pad all boundaries equally.
Two values, one for each
(X, Y)axis, to apply symmetric padding to each axis independently.Three values, one for each
(X, Y, Z)axis, to apply symmetric padding to each axis independently.Four values, one for each
(-X, +X, -Y, +Y)boundary, to apply padding to each boundary independently.Six values, one for each
(-X, +X, -Y, +Y, -Z, +Z)boundary, to apply padding to each boundary independently.
The specified value is the maximum padding that may be applied. If the padding extends beyond the actual extents of this mesh, it is clipped and does not extend outside the bounds of the image.
- background_value
float|VectorLike[float],optional Value or multi-component vector considered to be the background. Only valid when using a mask to crop the image.
- keep_dimensionsbool, default:
False If
True, the cropped output ispaddedwithfill_valueto ensure the output dimensions match the input.- fill_value
float|VectorLike[float],optional Value used when padding the cropped output if
keep_dimensionsisTrue. May be a single float or a multi-component vector (e.g. RGB vector).- rebase_coordinatesbool, default:
False Rebase the coordinate reference of the cropped output:
The rebasing effectively applies a positive translation in world (XYZ) coordinates and a similar (i.e. inverse) negative translation in voxel (IJK) coordinates. As a result, the
boundsof the output are unchanged, but the coordinate reference frame is modified.Set this to
Falseto leave the origin unmodified and keep the offset used by the crop.- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- factor
- Returns:
ImageDataCropped image.
See also
pad_imageAdd points to image boundaries. This is the inverse operation of the
margincrop.resampleModify an image’s dimensions and spacing.
select_valuesThreshold-like filter which may be used to generate a mask for cropping.
extract_subsetEquivalent filter to
crop(extent=voi, rebase_coordinates=True).- Crop Labeled ImageData
Example cropping
ImageDatausing a segmentation mask.
Examples
Load a grayscale image.
>>> import numpy as np >>> import pyvista as pv >>> from pyvista import examples >>> gray_image = examples.download_yinyang() >>> gray_image.dimensions (512, 342, 1)
Define a custom plotting helper to show the image as pixel cells.
>>> def image_plotter(image): ... pixel_cells = image.points_to_cells() ... ... pl = pv.Plotter() ... pl.add_mesh( ... pixel_cells, ... cmap='gray', ... clim=[0, 255], ... lighting=False, ... show_scalar_bar=False, ... ) ... pl.view_xy() ... pl.camera.tight() ... return pl
Plot the image for context.
>>> image_plotter(gray_image).show()

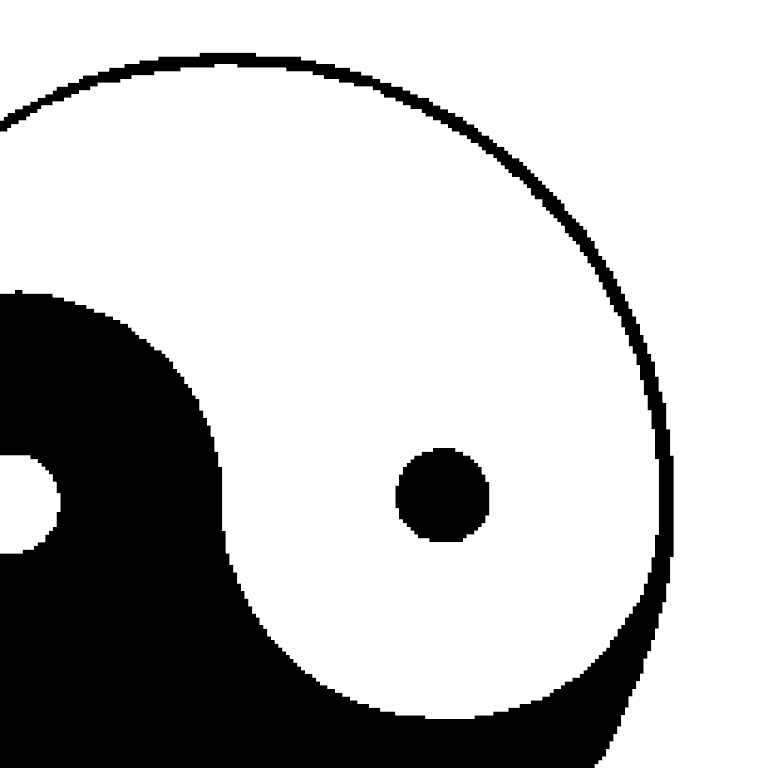
Crop the white border around the image using active scalars as a mask. Here we specify a background value of
255to correspond to white pixels. If this was an RGB image, we could also specify(255, 255, 255)as the background value.>>> cropped = gray_image.crop(mask=True, background_value=255) >>> cropped.dimensions (237, 238, 1) >>> image_plotter(cropped).show()
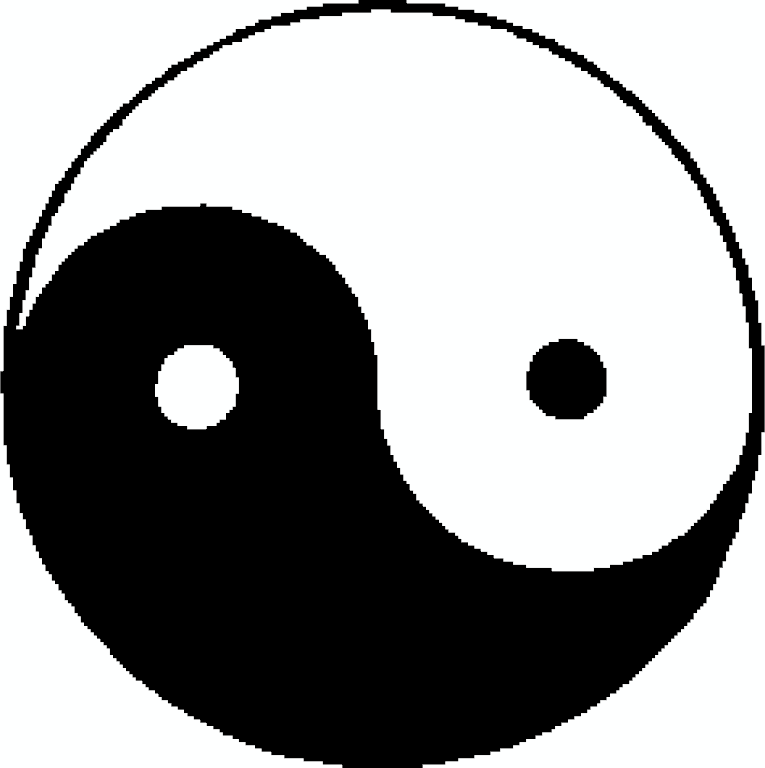
Use
margininstead to remove 100 and 20 pixels from each side of the x- and y-axis, respectively.>>> cropped = gray_image.crop(margin=(100, 20)) >>> cropped.dimensions (312, 302, 1) >>> image_plotter(cropped).show()
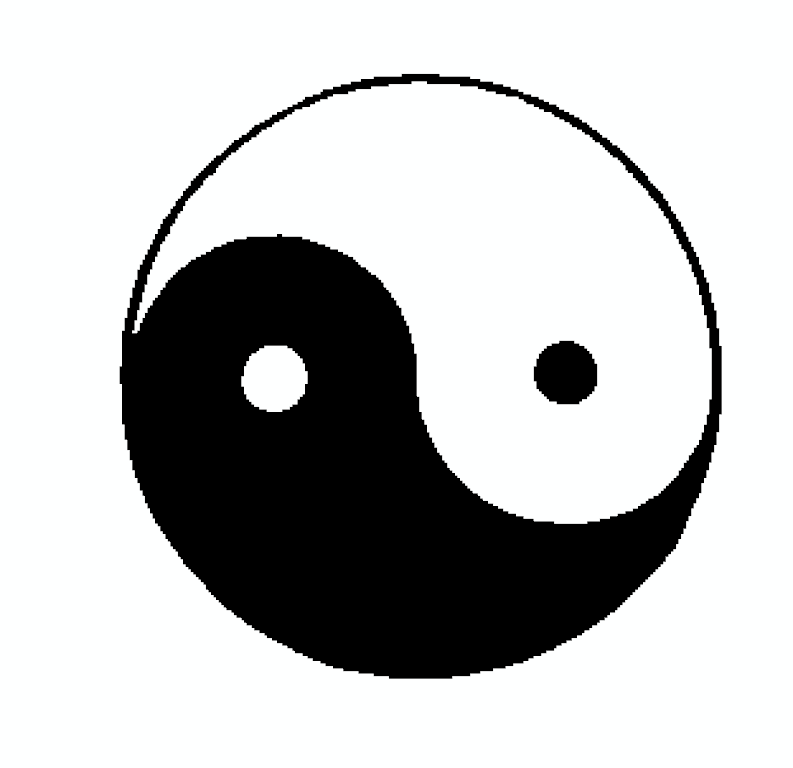
Use
offsetto select a starting location for the crop (from the origin at the bottom-left corner) along withdimensionsto define the crop size.>>> cropped = gray_image.crop(offset=(50, 20, 0), dimensions=(300, 200, 1)) >>> cropped.dimensions (300, 200, 1) >>> image_plotter(cropped).show()

Use
extentdirectly instead of usingdimensionsandoffsetto yield the same result as above.>>> cropped = gray_image.crop(extent=(50, 349, 20, 219, 0, 0)) >>> cropped.extent (50, 349, 20, 219, 0, 0) >>> image_plotter(cropped).show()

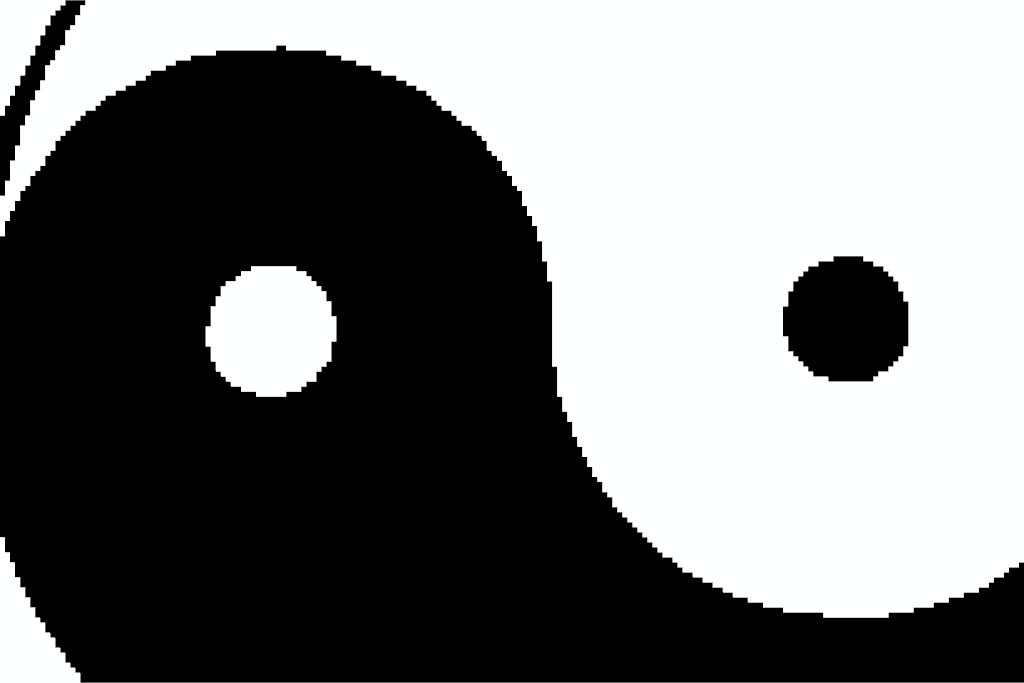
Use
factorto crop 40% of the image. This keeps 40% of the pixels along each axis, and removes 60% (i.e. 30% from each side).>>> cropped = gray_image.crop(factor=0.4) >>> cropped.dimensions (204, 136, 1) >>> image_plotter(cropped).show()
Use
normalized_boundsto crop from 40% to 80% of the image along the x-axis, and from 30% to 90% of the image along the y-axis.>>> cropped = gray_image.crop(normalized_bounds=[0.4, 0.8, 0.3, 0.9, 0.0, 1.0]) >>> cropped.extent (205, 408, 103, 306, 0, 0) >>> image_plotter(cropped).show()