Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
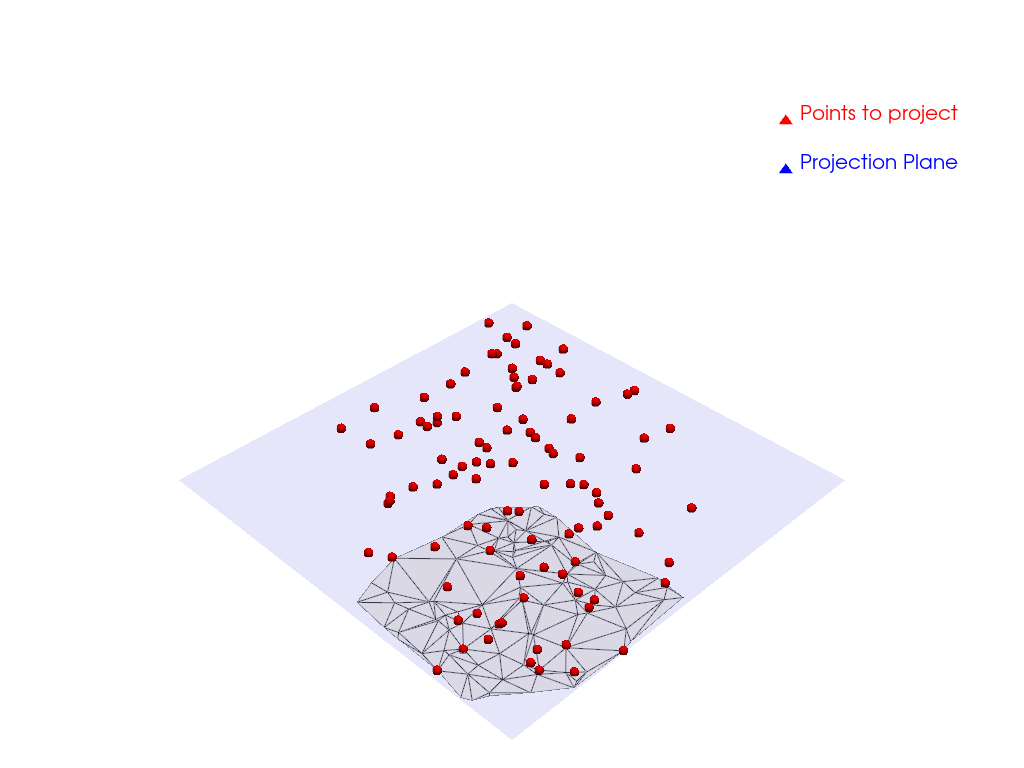
Project points to a plane and Tessellate#
Using pyvista and numpy, generate a 3D point cloud, project it to a plane, and tessellate it.
This demonstrates how to use
pyvista.UnstructuredGridFilters.delaunay_2d and a simple numpy
function that projects points to a plane.
from __future__ import annotations
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
Project Points#
Create a point cloud and project it to a plane.
num_points = 100
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0) # Seed rng for reproducibility
point_cloud = rng.random((num_points, 3))
# Define a plane
origin = [0, 0, 0]
normal = [0, 0, 1]
plane = pv.Plane(center=origin, direction=normal)
def project_points_to_plane(points, plane_origin, plane_normal):
"""Project points to a plane."""
vec = points - plane_origin
dist = np.dot(vec, plane_normal)
return points - np.outer(dist, plane_normal)
projected_points = project_points_to_plane(point_cloud, origin, normal)
# Create a polydata object with projected points
polydata = pv.PolyData(projected_points)
# Mesh using delaunay_2d and pyvista
mesh = polydata.delaunay_2d()
Visualize the Result#
# Create a plane for visualization
plane_vis = pv.Plane(
center=origin,
direction=normal,
i_size=2,
j_size=2,
i_resolution=10,
j_resolution=10,
)
# plot it
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(mesh, show_edges=True, color='white', opacity=0.5, label='Tessellated mesh')
pl.add_mesh(
pv.PolyData(point_cloud),
color='red',
render_points_as_spheres=True,
point_size=10,
label='Points to project',
)
pl.add_mesh(plane_vis, color='blue', opacity=0.1, label='Projection Plane')
pl.add_legend()
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.352 seconds)