Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Creating a Structured Surface#
Create a StructuredGrid surface from NumPy arrays
using pyvista.StructuredGrid.
from __future__ import annotations
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
From NumPy Meshgrid#
Create a simple meshgrid using NumPy
Now pass the NumPy meshgrid to PyVista
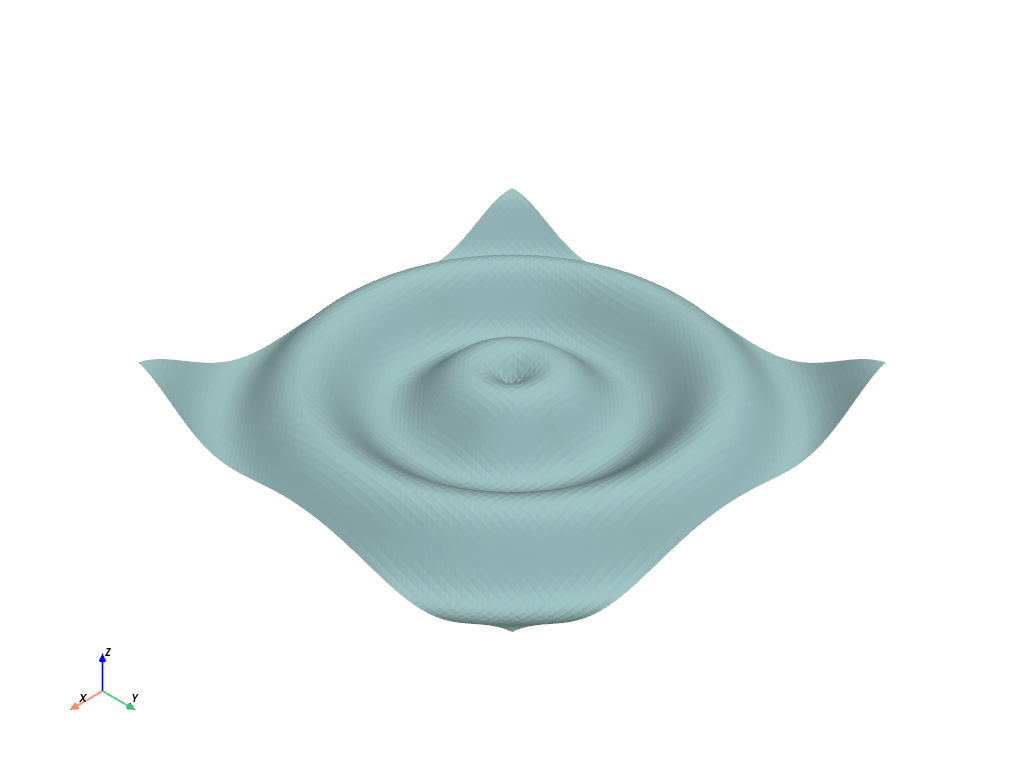
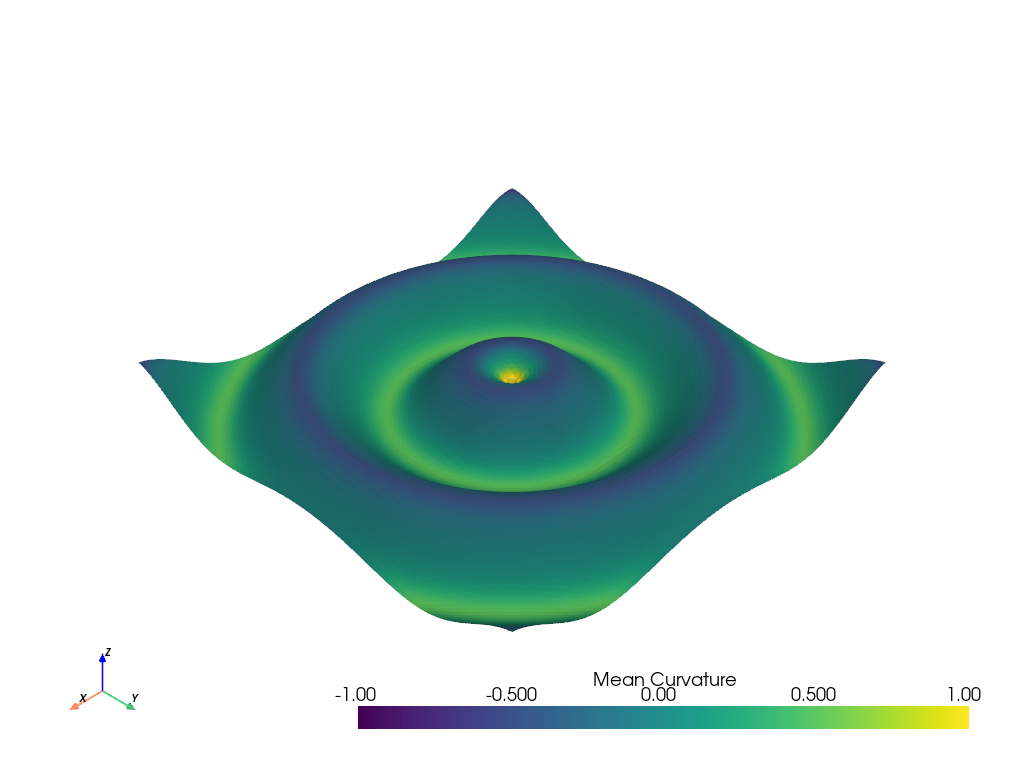
# Plot mean curvature as well
grid.plot_curvature(clim=[-1, 1])
Generating a structured grid is a one-liner in this module, and the points from the resulting surface can be accessed as a NumPy array:
grid.points
pyvista_ndarray([[-10. , -10. , 0.99998766],
[-10. , -9.75 , 0.98546793],
[-10. , -9.5 , 0.9413954 ],
...,
[ 9.75 , 9.25 , 0.76645876],
[ 9.75 , 9.5 , 0.86571785],
[ 9.75 , 9.75 , 0.93985707]])
From XYZ Points#
Quite often, you might be given a set of coordinates (XYZ points) in a simple tabular format where there exists some structure such that grid could be built between the nodes you have. A great example is found in pyvista-support#16 where a structured grid that is rotated from the cartesian reference frame is given as just XYZ points. In these cases, all that is needed to recover the grid is the dimensions of the grid (nx by ny by nz) and that the coordinates are ordered appropriately.
For this example, we will create a small dataset and rotate the coordinates such that they are not on orthogonal to cartesian reference frame.
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)
def make_point_set():
"""Return an n by 3 numpy array of structured coordinates.
The contents of this function can be ignored.
"""
n, m = 29, 32
x = np.linspace(-200, 200, num=n) + rng.uniform(-5, 5, size=n)
y = np.linspace(-200, 200, num=m) + rng.uniform(-5, 5, size=m)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
A, b = 100, 100
zz = A * np.exp(-0.5 * ((xx / b) ** 2.0 + (yy / b) ** 2.0))
points = np.c_[xx.reshape(-1), yy.reshape(-1), zz.reshape(-1)]
foo = pv.PolyData(points)
foo.rotate_z(36.6, inplace=True)
return foo.points
# Get the points as a 2D NumPy array (N by 3)
points = make_point_set()
points[0:5, :]
pyvista_ndarray([[ -41.11604332, -277.78395702, 1.93953334],
[ -32.59496709, -271.45564733, 2.38128479],
[ -22.96309829, -264.30239027, 2.96245204],
[ -11.69053308, -255.93064453, 3.75584021],
[ 6.17467684, -242.66276872, 5.25406934]])
Now pretend that the (n by 3) NumPy array above are coordinates that you have, possibly from a file with three columns of XYZ points.
We simply need to recover the dimensions of the grid that these points make
and then we can generate a pyvista.StructuredGrid mesh.
Let’s preview the points to see what we are dealing with:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.scatter(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], c=points[:, 2])
plt.axis('image')
plt.xlabel('X Coordinate')
plt.ylabel('Y Coordinate')
plt.show()
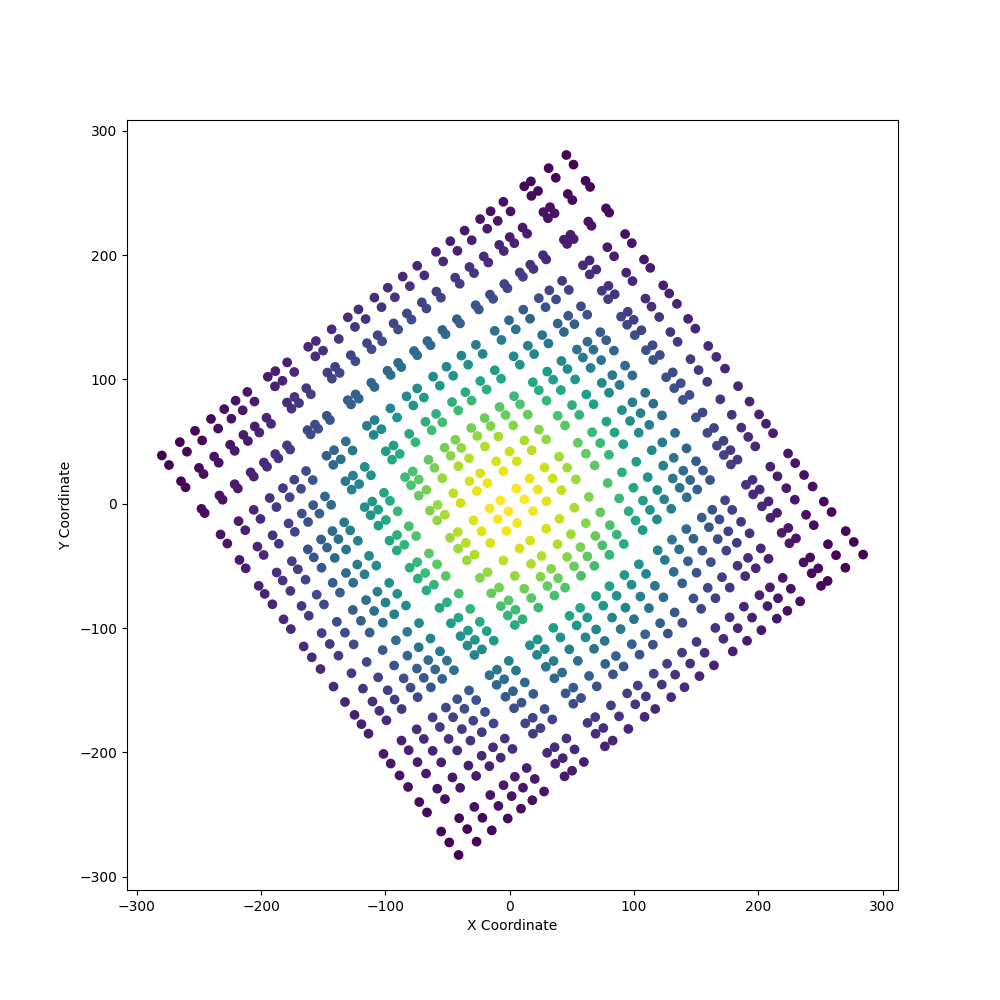
In the figure above, we can see some inherit structure to the points and thus
we could connect the points as a structured grid. All we need to know are the
dimensions of the grid present. In this case, we know (because we made this
dataset) the dimensions are [29, 32, 1], but you might not know the
dimensions of your pointset. There are a few ways to figure out the
dimensionality of structured grid including:
manually counting the nodes along the edges of the pointset
using a technique like principle component analysis to strip the rotation from the dataset and count the unique values along each axis for the new;y projected dataset.
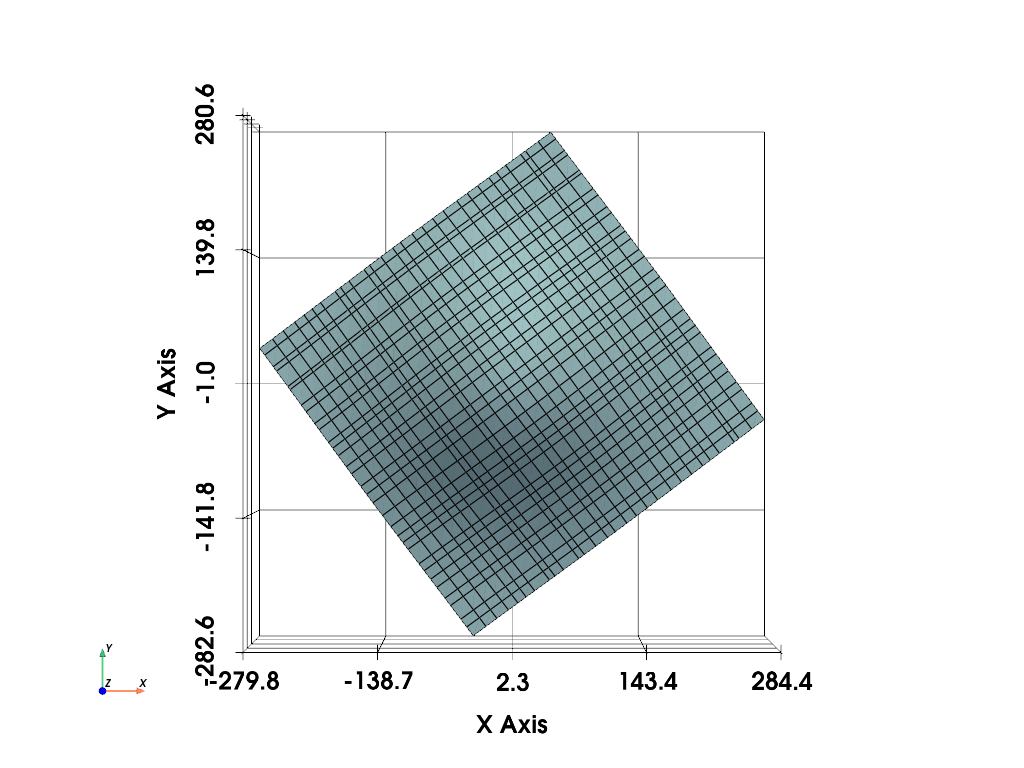
# Once you've figured out your grid's dimensions, simple create the
# :class:`pyvista.StructuredGrid` as follows:
mesh = pv.StructuredGrid()
# Set the coordinates from the numpy array
mesh.points = points
# set the dimensions
mesh.dimensions = [29, 32, 1]
# and then inspect it
mesh.plot(show_edges=True, show_grid=True, cpos='xy')
Extending a 2D StructuredGrid to 3D#
A 2D pyvista.StructuredGrid mesh can be extended into a 3D mesh.
This is highly applicable when wanting to create a terrain following mesh
in earth science research applications.
For example, we could have a pyvista.StructuredGrid of a topography
surface and extend that surface to a few different levels and connect each
“level” to create the 3D terrain following mesh.
Let’s start with a simple example by extending the wave mesh to 3D
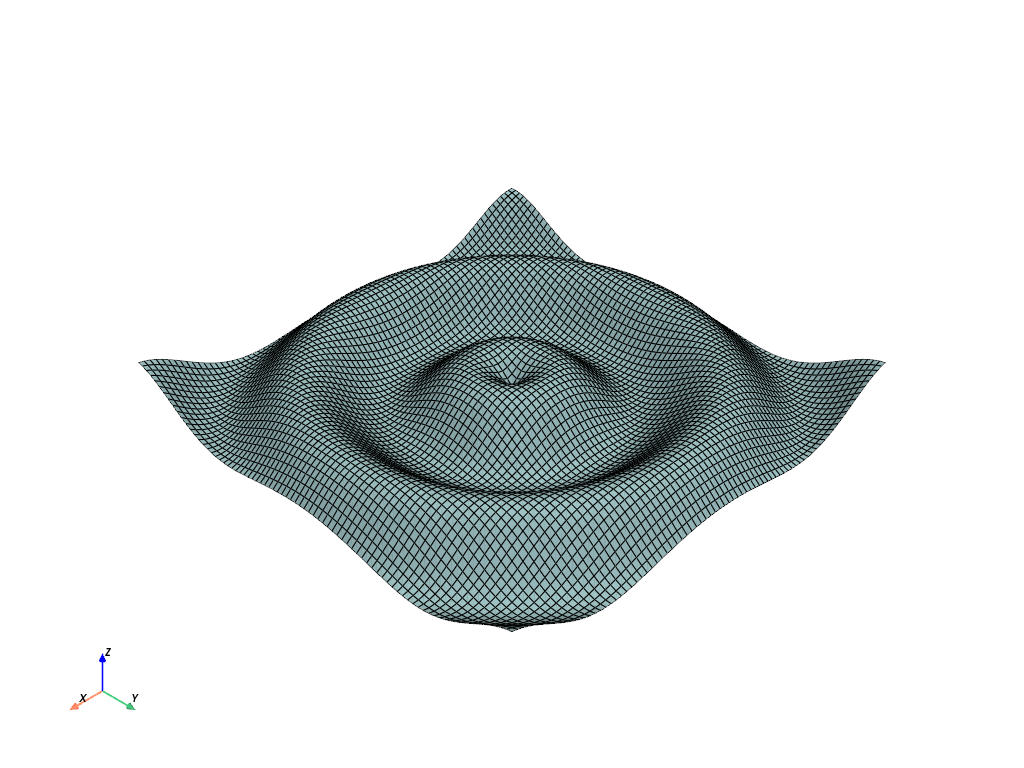
struct = examples.load_structured()
struct.plot(show_edges=True)
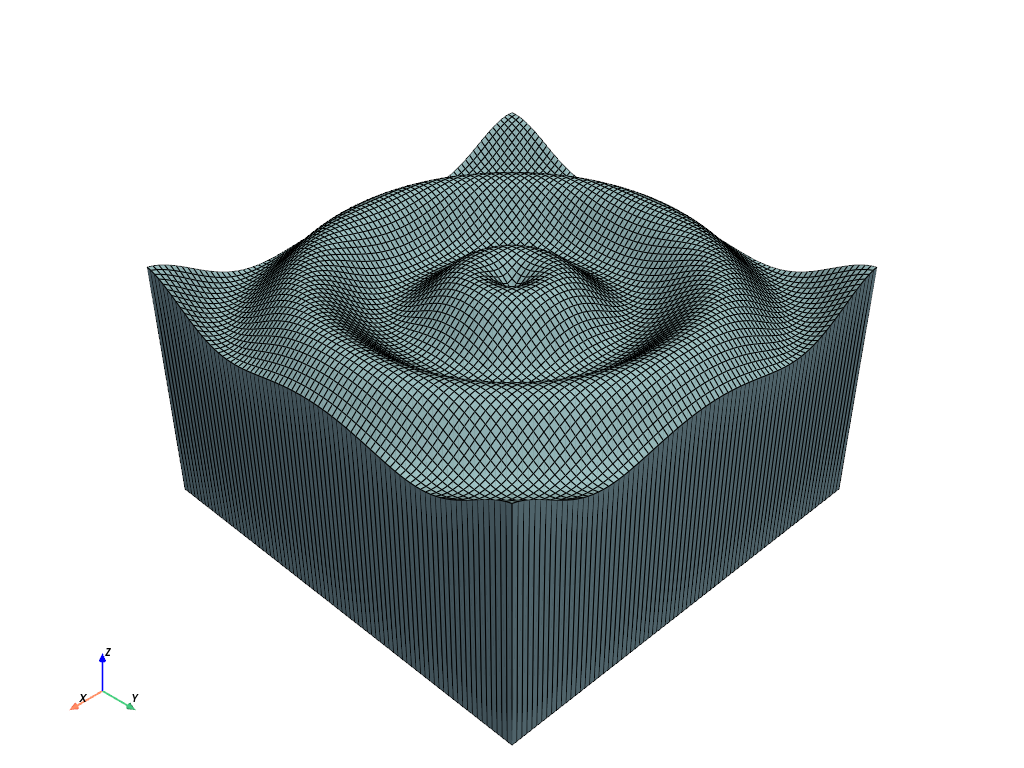
top = struct.points.copy()
bottom = struct.points.copy()
bottom[:, -1] = -10.0 # Wherever you want the plane
vol = pv.StructuredGrid()
vol.points = np.vstack((top, bottom))
vol.dimensions = [*struct.dimensions[0:2], 2]
vol.plot(show_edges=True)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.958 seconds)