Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Create a GIF Movie#
Generate a moving gif from an active plotter.
This example uses open_gif() and
write_frame() to create the gif.
Note
Use lighting=False to reduce the size of the color space to avoid
“jittery” GIFs, especially for the scalar bar.
from __future__ import annotations
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
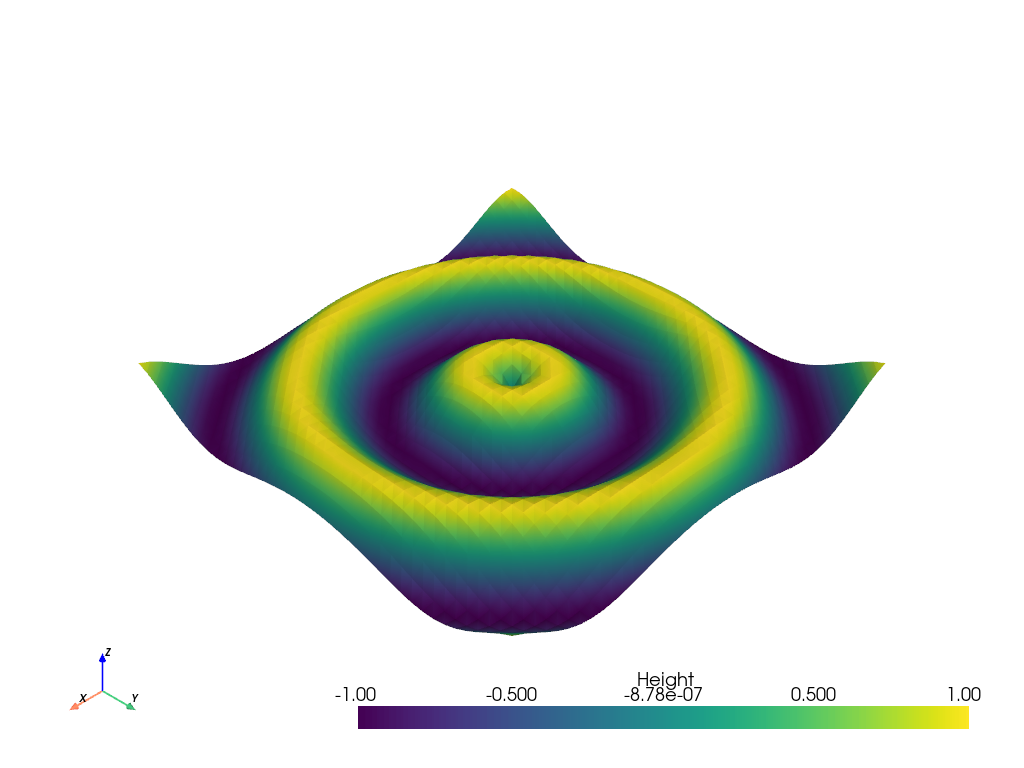
Create a structured grid#
Create a structured grid and make a “wave” my shifting the Z position based on the cartesian distance from the origin.
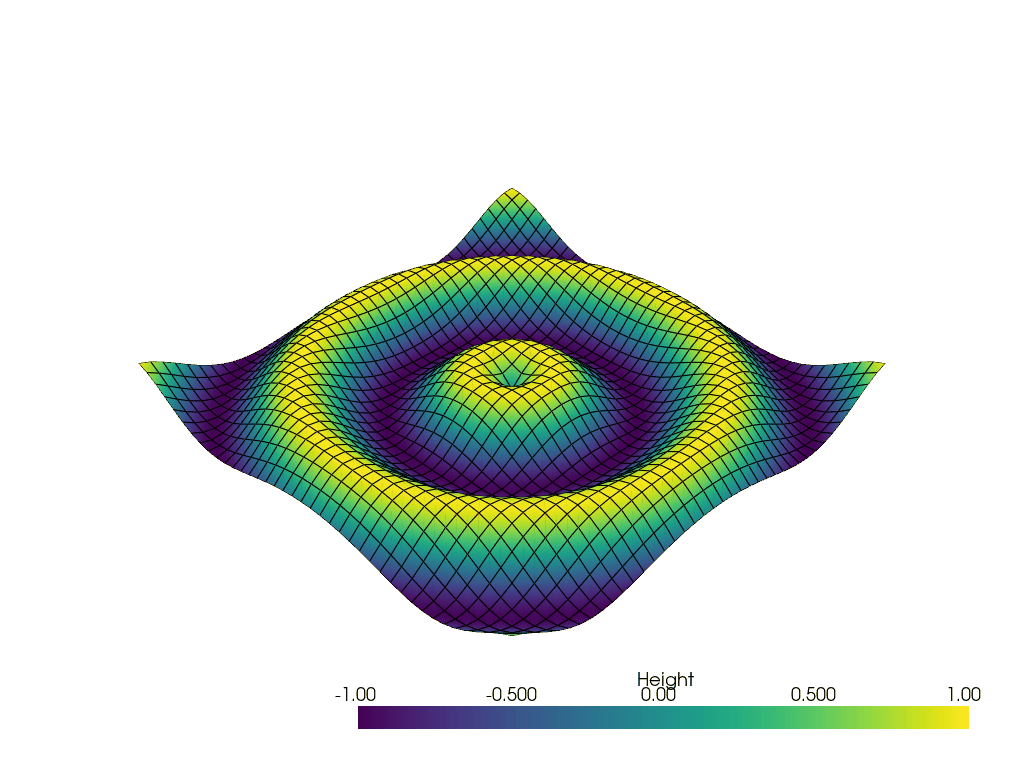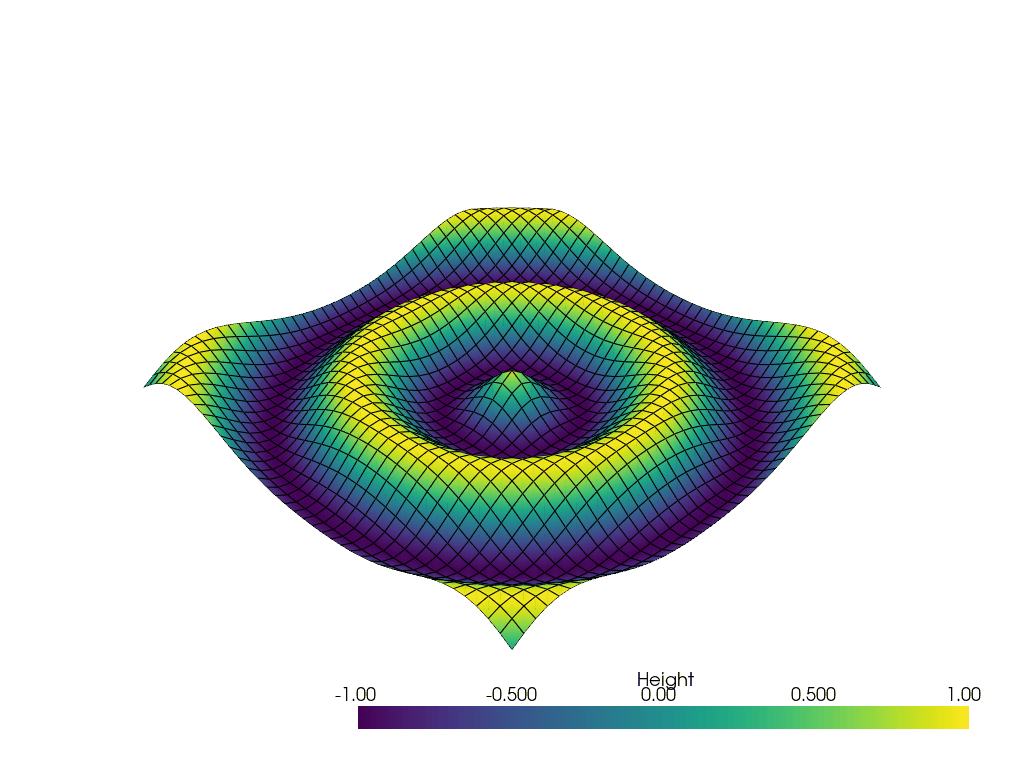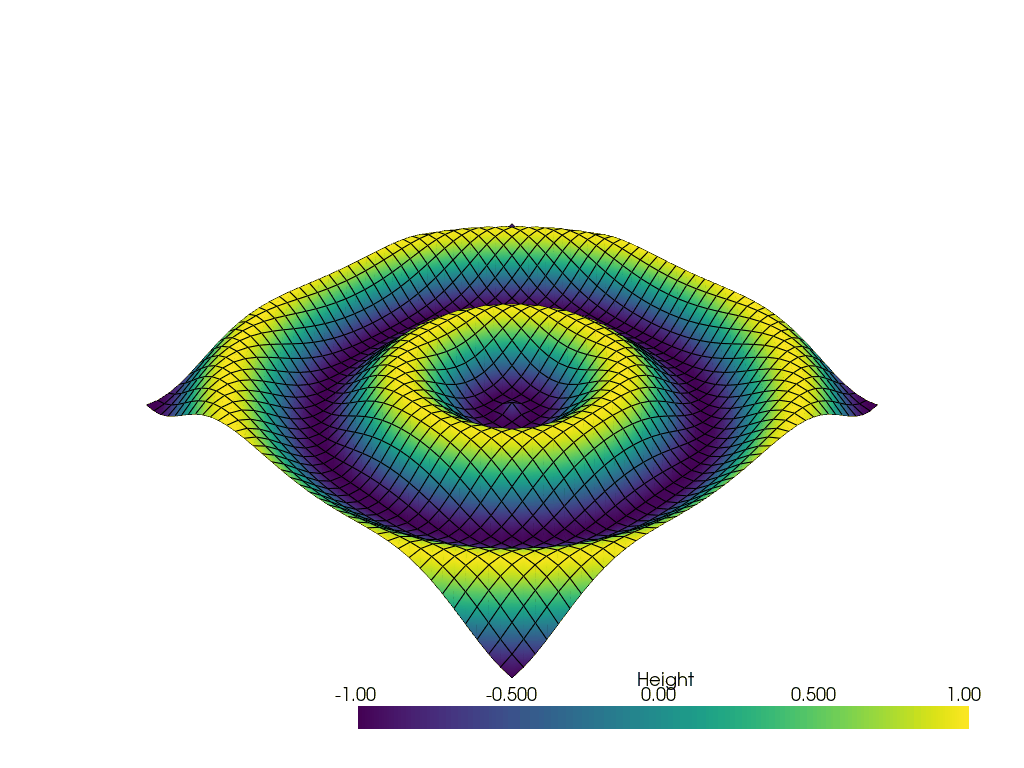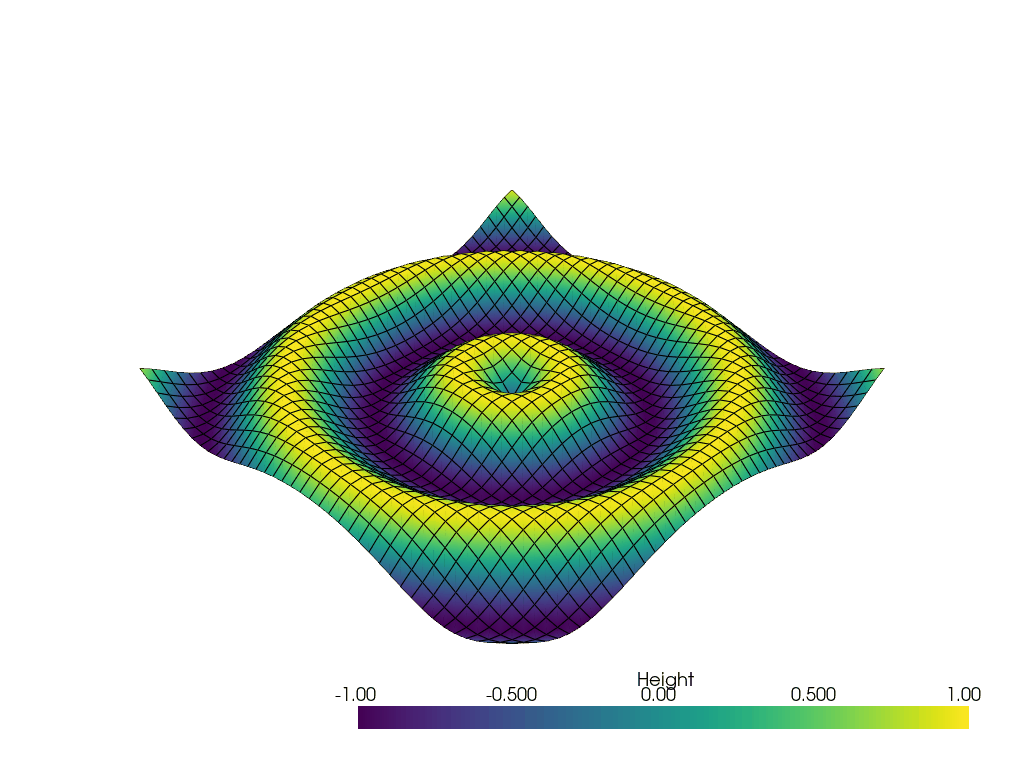
Generate a GIF#
Generate a GIF using off_screen=True parameter.
# Create a plotter object and set the scalars to the Z height
pl = pv.Plotter(notebook=False, off_screen=True)
pl.add_mesh(
grid,
scalars='Height',
lighting=False,
show_edges=True,
clim=[-1, 1],
)
# Open a gif
pl.open_gif('wave.gif')
# Update Z and write a frame for each updated position
nframe = 15
for phase in np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, nframe + 1)[:nframe]:
z = np.sin(r + phase)
# Update values inplace
grid.points[:, -1] = z.ravel()
grid['Height'] = z.ravel()
# Write a frame. This triggers a render.
pl.write_frame()
# Closes and finalizes movie
pl.close()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.773 seconds)