pyvista.PolyDataFilters.smooth_taubin#
- PolyDataFilters.smooth_taubin(n_iter=20, pass_band=0.1, edge_angle=15.0, feature_angle=45.0, boundary_smoothing=True, feature_smoothing=False, non_manifold_smoothing=False, normalize_coordinates=False, inplace=False, progress_bar=False)[source]#
Smooth a PolyData DataSet with Taubin smoothing.
This filter allows you to smooth the mesh as in the Laplacian smoothing implementation in
smooth(). However, unlike Laplacian smoothing the surface does not “shrink” since this filter relies on an alternative approach to smoothing. This filter is more akin to a low pass filter where undesirable high frequency features are removed.This PyVista filter uses the VTK vtkWindowedSincPolyDataFilter filter.
- Parameters:
- n_iter
int, default: 20 This is the degree of the polynomial used to approximate the windowed sync function. This is generally much less than the number needed by
smooth().- pass_band
float, default: 0.1 The passband value for the windowed sinc filter. This should be between 0 and 2, where lower values cause more smoothing.
- edge_angle
float, default: 15.0 Edge angle to control smoothing along edges (either interior or boundary).
- feature_angle
float, default: 45.0 Feature angle for sharp edge identification.
- boundary_smoothingbool, default:
True Flag to control smoothing of boundary edges. When
True, boundary edges remain fixed.- feature_smoothingbool, default:
False Flag to control smoothing of feature edges. When
True, boundary edges remain fixed as defined byfeature_angleandedge_angle.- non_manifold_smoothingbool, default:
False Smooth non-manifold points.
- normalize_coordinatesbool, default:
False Flag to control coordinate normalization. To improve the numerical stability of the solution and minimize the scaling of the translation effects, the algorithm can translate and scale the position coordinates to within the unit cube
[-1, 1], perform the smoothing, and translate and scale the position coordinates back to the original coordinate frame.- inplacebool, default:
False Updates mesh in-place.
- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- n_iter
- Returns:
pyvista.PolyDataSmoothed mesh.
Notes
For maximum performance, do not enable
feature_smoothingorboundary_smoothing.feature_smoothingis especially expensive.References
See Optimal Surface Smoothing as Filter Design for details regarding the implementation of Taubin smoothing.
Examples
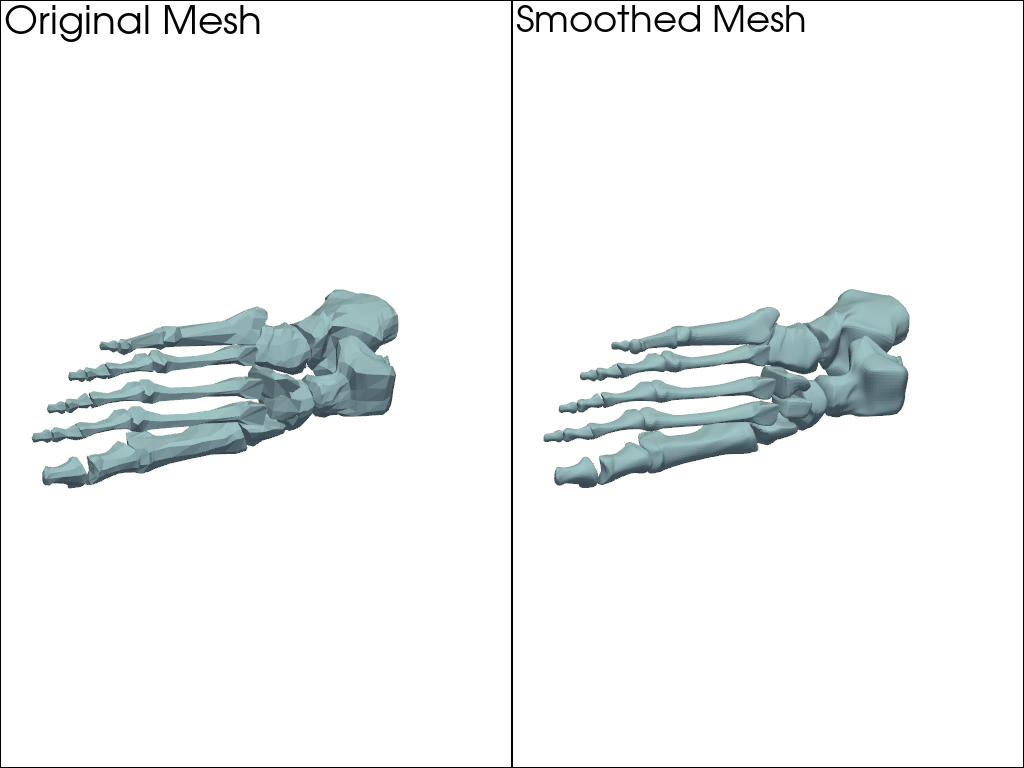
Smooth the example bone mesh. Here, it’s necessary to subdivide the mesh to increase the number of faces as the original mesh is so coarse.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> from pyvista import examples >>> mesh = examples.download_foot_bones().subdivide(2) >>> smoothed_mesh = mesh.smooth_taubin() >>> pl = pv.Plotter(shape=(1, 2)) >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(mesh) >>> _ = pl.add_text('Original Mesh') >>> pl.subplot(0, 1) >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(smoothed_mesh) >>> _ = pl.add_text('Smoothed Mesh') >>> pl.show()
See Surface Smoothing for more examples using this filter.