pyvista.DataSetFilters.clip_surface#
- DataSetFilters.clip_surface(surface, invert=True, value=0.0, compute_distance=False, progress_bar=False, crinkle=False)[source]#
Clip any mesh type using a
pyvista.PolyDatasurface mesh.This will return a
pyvista.UnstructuredGridof the clipped mesh. Geometry of the input dataset will be preserved where possible. Geometries near the clip intersection will be triangulated/tessellated.- Parameters:
- surface
pyvista.PolyData The
PolyDatasurface mesh to use as a clipping function. If this input mesh is not a :class`pyvista.PolyData`, the external surface will be extracted.- invertbool, default:
True Flag on whether to flip/invert the clip.
- value
float, default: 0.0 Set the clipping value of the implicit function (if clipping with implicit function) or scalar value (if clipping with scalars).
- compute_distancebool, default:
False Compute the implicit distance from the mesh onto the input dataset. A new array called
'implicit_distance'will be added to the output clipped mesh.- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- crinklebool, default:
False Crinkle the clip by extracting the entire cells along the clip. This adds the
"cell_ids"array to thecell_dataattribute that tracks the original cell IDs of the original dataset.
- surface
- Returns:
pyvista.PolyDataClipped surface.
Examples
Clip a cube with a sphere.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> sphere = pv.Sphere(center=(-0.4, -0.4, -0.4)) >>> cube = pv.Cube().triangulate().subdivide(3) >>> clipped = cube.clip_surface(sphere) >>> clipped.plot(show_edges=True, cpos='xy', line_width=3)
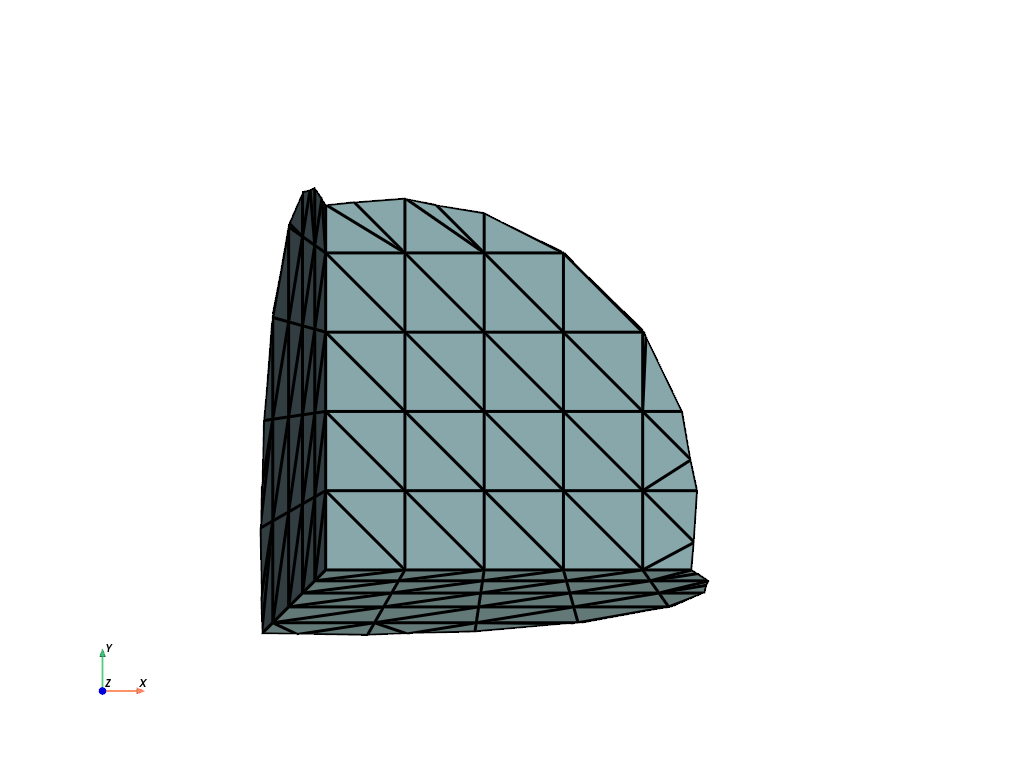
See Clipping with a Surface for more examples using this filter.